History of Transactive Energy Program
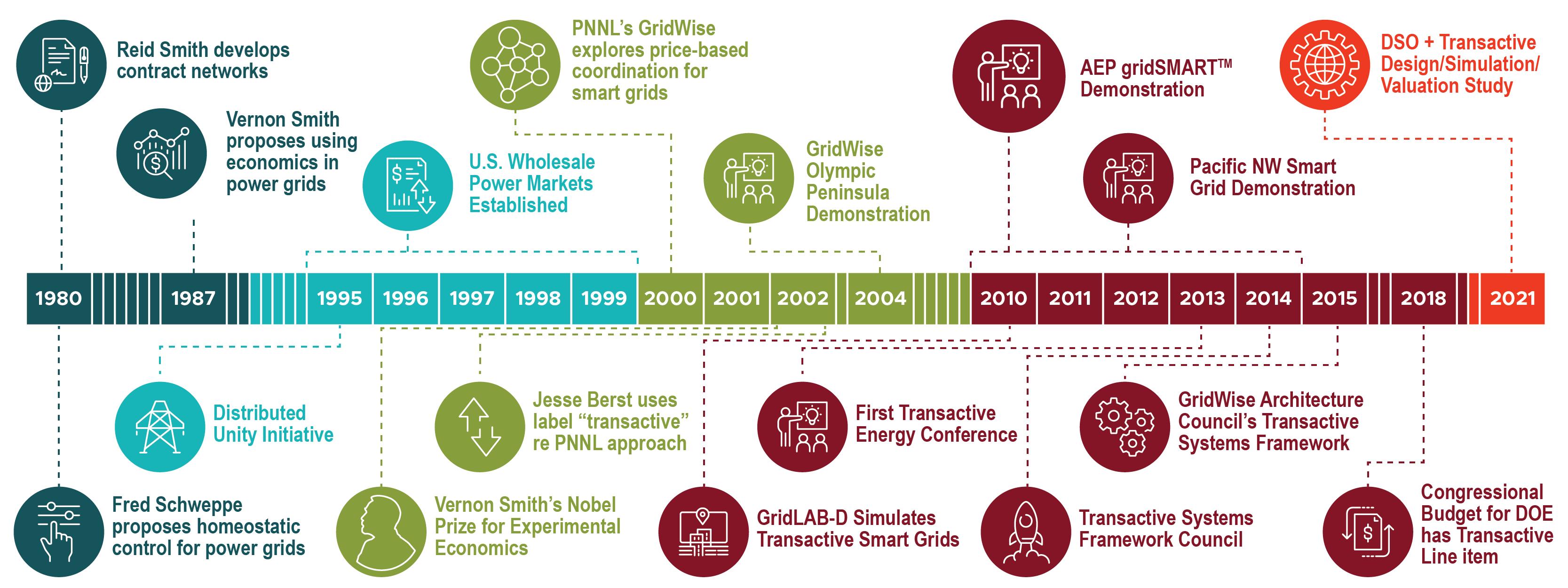
Distributed decision-making concepts applied to industrial controls emerged in the 1980s. Reid Smith proposed efficient multi-processing computer loading algorithms with the contract net protocol. More directly related to electric power, Fred Schweppe and colleagues proposed energy market-based, homeostatic control for power systems. PNNL began to explore dynamic pricing-based transactions as a key coordination scheme and launched the GridWise Initiative in 2000.
The term “transactive” was first applied to PNNL’s approach shortly thereafter by Jesse Berst, publisher of the Smart Grid News, who observed the internet evolved from passive sharing of static information to allowing active dynamic websites and eventually supporting business transactions.
Key PNNL Transactive Energy Projects
GridWise® Olympic Peninsula Demonstration (2006-07)
In 2006 through early 2007, the GridWise™ Demonstration Projects pioneered the transactive approach. The project demonstrated use of advanced information-based technologies to increase power grid efficiency, reliability, and flexibility while reducing the need to build additional infrastructure.
AEP gridSMART Demonstration Project
The AEP project was funded under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA). The effort extended the transactive energy approach to approximately 200 homes and connected them to regional generation and transmission congestion costs via a retail price signal that reflected wholesale market prices. For the first time, a utility and its Public Utility Commission were formally engaged in developing and approving a fair and equitable transactive rate design.
Pacific Northwest Smart Grid Demonstration Project
The Pacific Northwest Smart Grid Demonstration Project, also funded under ARRA, extended the transactive approach to a regional level involving five states. The project employed a transactive signal to engage an array of assets, ranging from demand response in residential, commercial, and institutional buildings to battery storage, distributed generation, and conservation voltage reduction and volt-VAR control schemes.