Autonomous Receivers
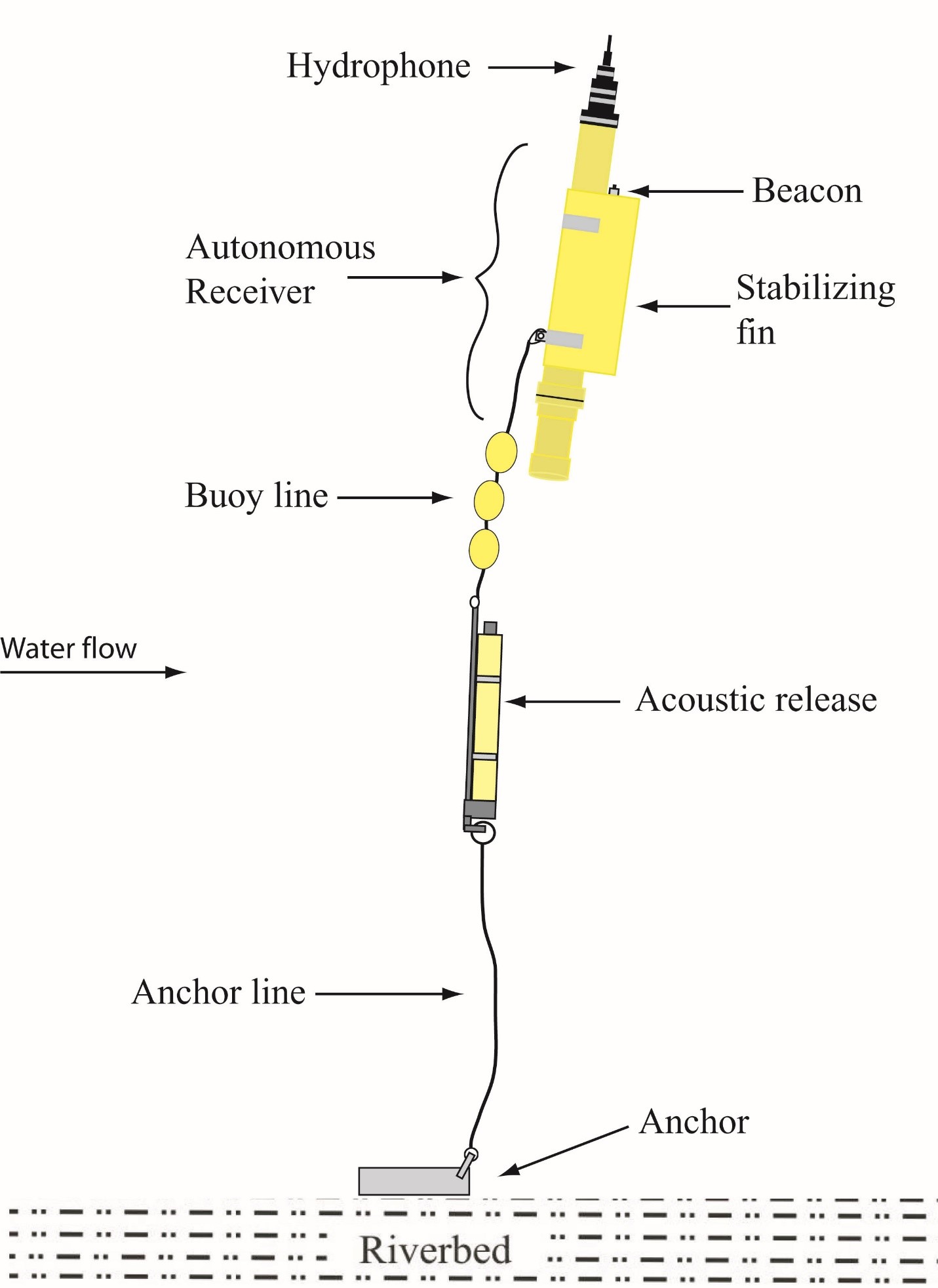
The autonomous receivers are self-contained and consist of a PVC housing with a threaded coupling and O-ring to join the upper and lower portions (Figure 1). The lower housing holds lithium battery packs capable of powering the receiver for 30 days. The upper housing has an externally mounted omnidirectional hydrophone on the top (Figure 2) and internal analog and digital circuit boards. Each receiver is fitted with an external beacon tag that transmits a unique code every 15 seconds, as well as a high-impact plastic fin to reduce drag and increase stability under high-flow conditions. Receivers record pressure and water temperature data every 15 seconds. All data are stored on Compact Flash media (1 GB, SanDisk Extreme III). Autonomous receivers are positively buoyant and typically deployed 3 to 5 m above the riverbed or ocean floor (Figure 3). System components designed specifically for use in the near-shore ocean are under development and have been tested successfully in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of Washington State. JSATS autonomous receivers have been produced by several commercial vendors, including Advanced Telemetry Systems, LOTEK Wireless, Sonic Concepts, Inc., and Teknologic.
Cloud-based, Real-time Autonomous Receivers
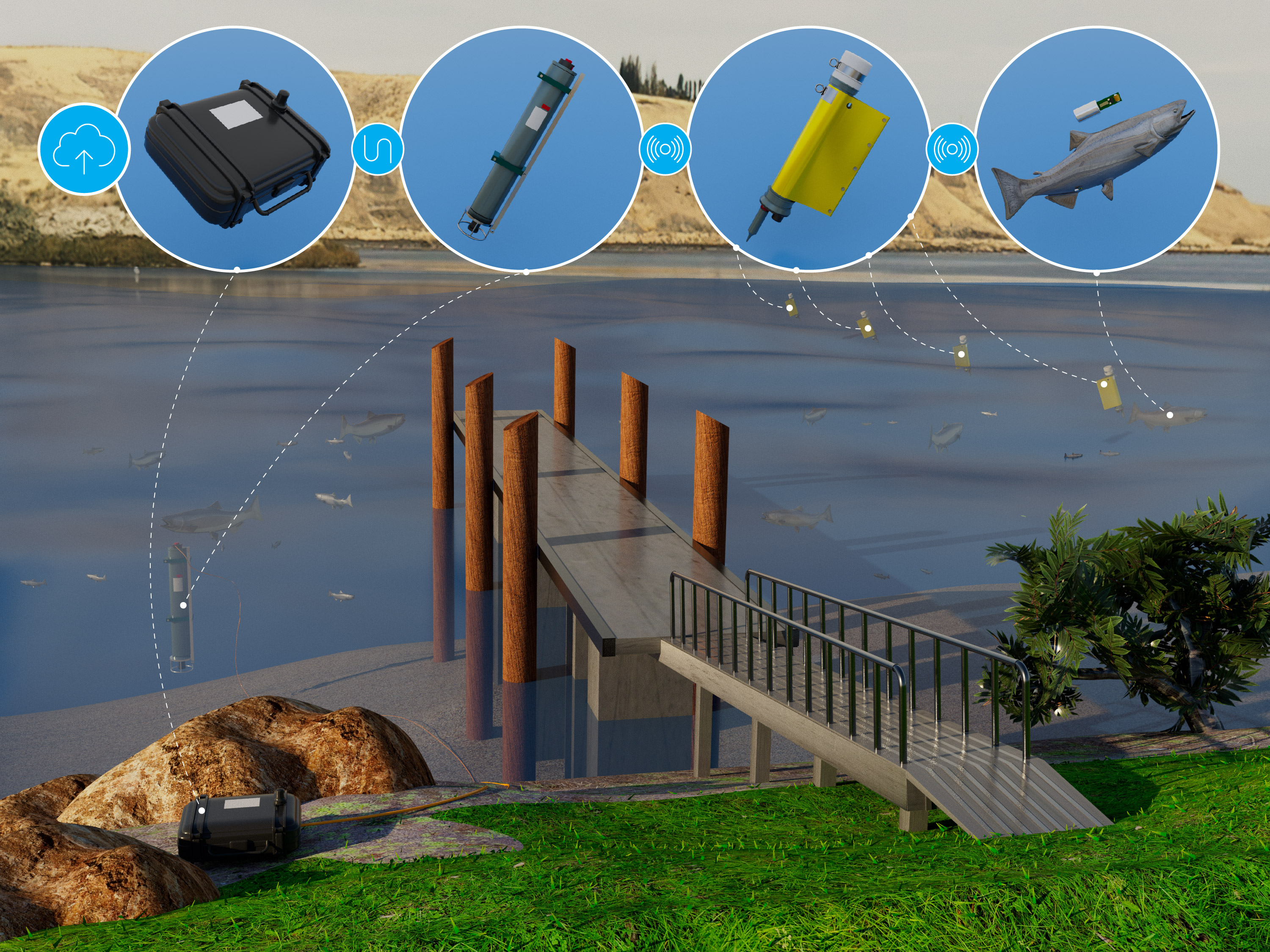

Current autonomous acoustic telemetry systems are unable to transmit data continuously in real-time due to limited acoustic networking bandwidth. We developed a cloud-based, real-time, autonomous acoustic telemetry system with edge computing capabilities. It allows for the real-time estimation of fish behavior, monitoring the health of the acoustic receivers, and monitoring environmental parameters. In field testing, the system demonstrated significantly improved performance and reduced energy consumption compared to a benchmark system without edge computing.
More information on autonomous receivers and their deployment can be found at: