Technical Approach
We are undertaking the following steps and reporting the following accomplishments:
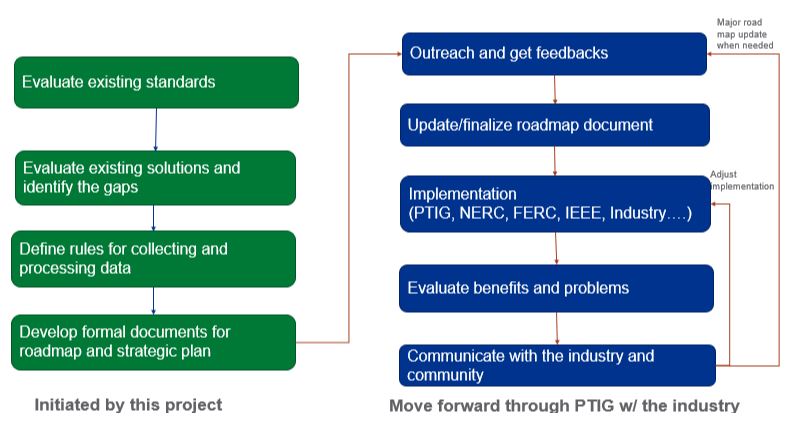
- Develop a comprehensive framework and roadmap for probabilistic planning and operations based on state-of-the art criteria, methodologies, software tools, and technologies (completed)
A Roadmap for Transition to Largely Probabilistic Methods - Eliminate the main gaps preventing a transition from deterministic to probabilistic methods: 1) lack of primary statistical information supporting the transition, and 2) lack of probabilistic reliability and performance standards. We have identified sources of information and standards that can be reviewed in terms of their transition to probabilistic framework.
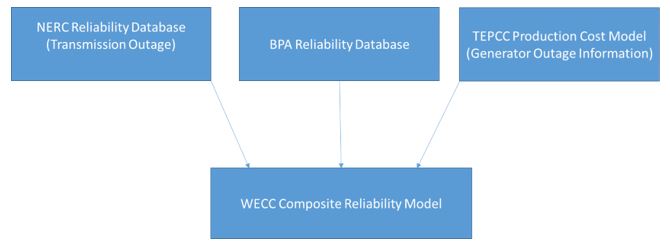
- Develop a composite probabilistic reliability model for the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) system completed, Fig. 1)
- Cooperate closely with the industry, Federal Energy Regulatory Council (FERC), North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), regulators, universities, government, national labs, software vendors, and other interested organizations to make sure that the best ideas, know-how, and skills are reflected in the framework and the roadmap (Ongoing activity)
Future work
- Initiate a nation-wide effort for implementing this framework as standard US practice in planning and operations (In progress + future work)
- Facilitate continuing education, dissemination, and technology transfer in the area of probabilistic methods and applications (Future work)
- Create and lead and Probabilistic Technology Interest Group (PTIG) as a tool to implement the Roadmap and forum for organization interested in the area. (Future work)
Fig 1. Building WECC system composite reliability model
Previous and related work
1. PNNL developed probabilistic models, methods and tools in the first phase of the project using OE funding
- A zonal geographically distributed model for the WECC system reflecting various sources of uncertainty.
- Probabilistic methods for separation of slow and fast power system motions and associated uncertainties to improve predictability and reduce uncertainty.
- Transmission Uncertainty and prediction Tool (TUT).
2. Adoption of previous work:
- SETO SunShot project with CAISO, Siemens, AWS Truepower (DOE+50% cost share)
- A project on uncertainty-based dynamic interchange adjustments (funded by ISO NE)
- Technology Commercialization project with CAISO and AWS Truepower (DOE OE and EERE)
- Central America projects (Department of State)
3. Still, we noticed and heard from the industry about the adoption barriers of probabilistic approaches
- Lack of sufficient primary statistical information and data
- Largely deterministic performance and reliability standards