Featured Stories
February 17, 2026
PNNL Powers Biotechnology, Grid Operations, Nuclear Science Through Genesis AI for Science Mission
February 11, 2026
Earthquake Data Provide Solid Footing for AI Foundation Science Model
January 27, 2026
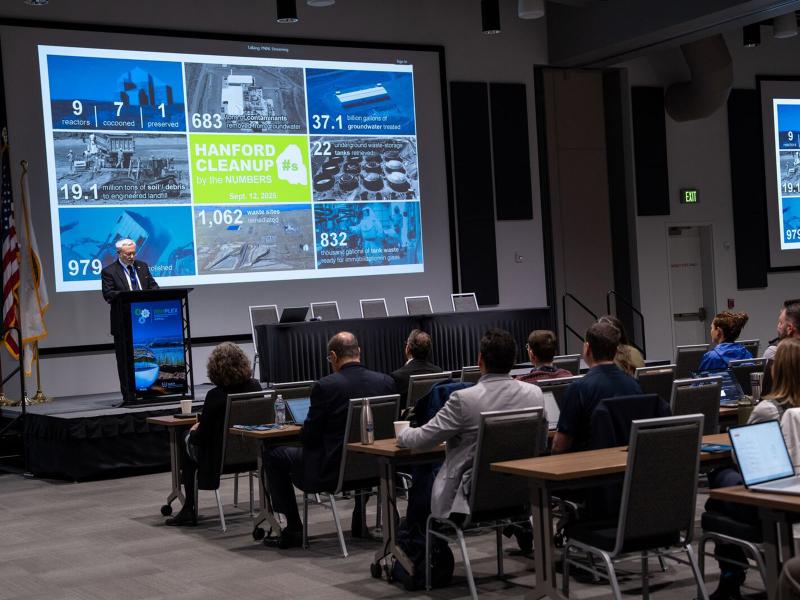
Nuclear Waste Transformed: PNNL Scientists Solidify History With Glass
January 29, 2026
New Minds for New Mines
Subscribe
to receive PNNL
news by email:
Latest Stories
1100 results found
Filters applied: Earth & Coastal Sciences, Chemical & Biothreat Signatures