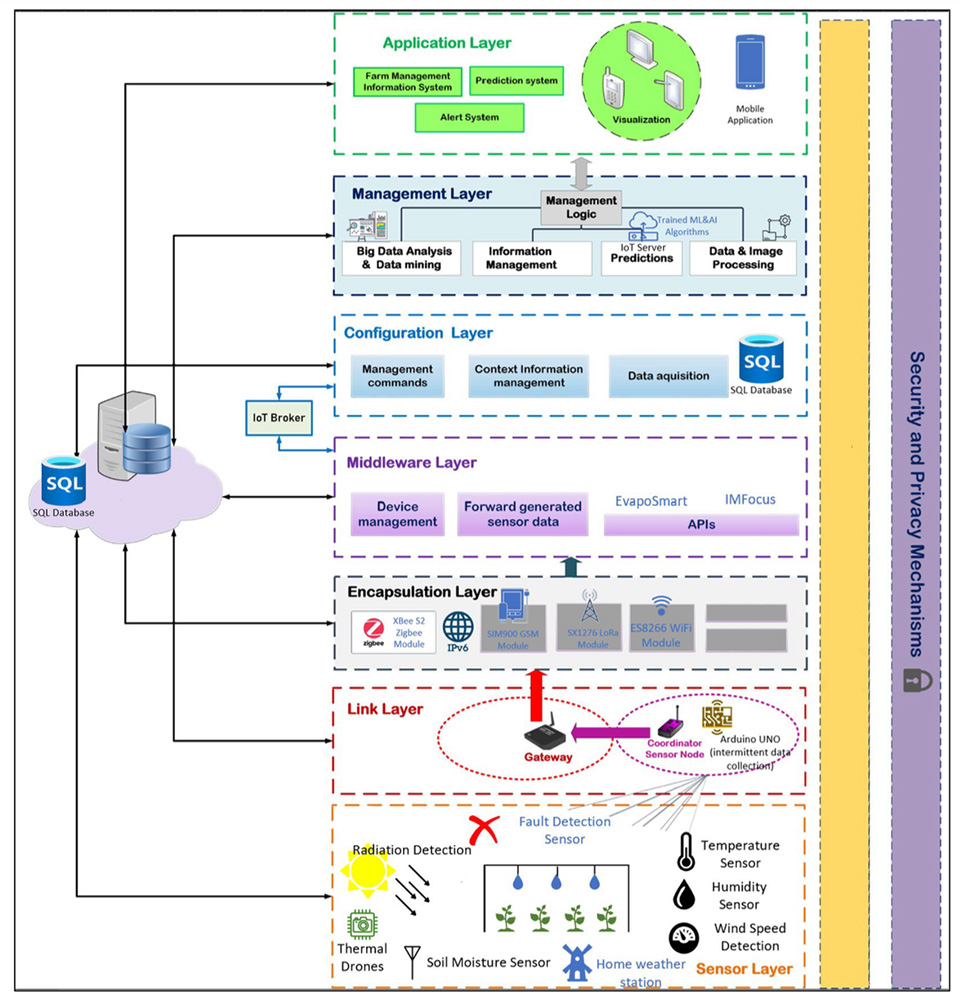
AI-Driven OH Security Projects
PNNL scientists are tackling the biggest scientific challenges to improve human, animal, plant, and environmental health while combating the emergence of infectious diseases. The Lab excels at harmonizing complex data with artificial intelligence (AI) from across domains, providers, and modalities to create valuable and trustworthy data-driven insights for decision-makers.
Below are projects the One Health (OH) team is tackling through key collaborations for situational awareness, early warning, and disease forecasting.
Situational awareness
Biofeeds is a biosurveillance platform for health threats to humans, animals, and plants. Monitoring chemical and biological threats, it uses open-source reports running on an AI-driven text analytic pipeline.
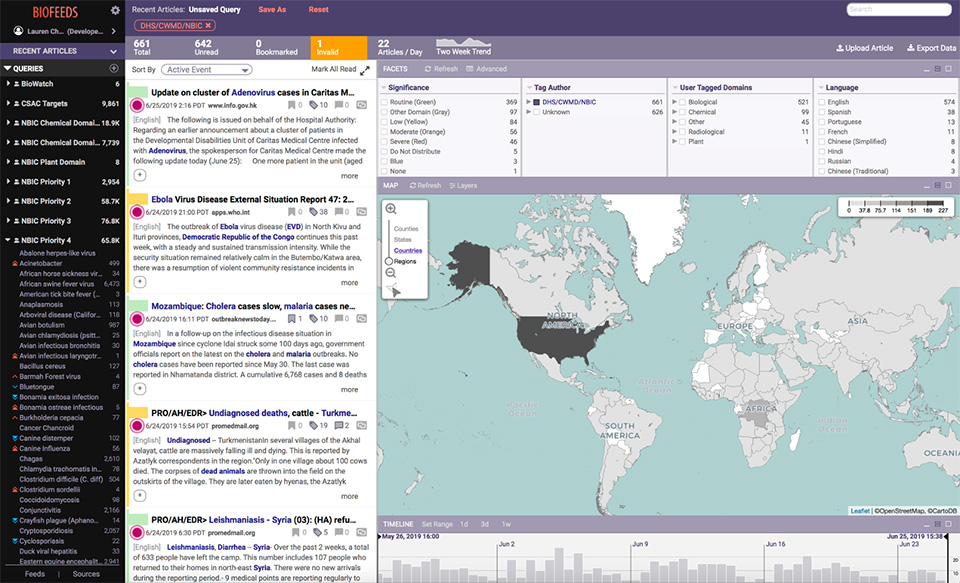
The Publication Literature Analysis and Text Interaction Platform for User Studies (PLATIPUS) was developed with funds from the COVID CARES ACT. The Department of Energy funded PNNL to build a public-facing, AI-driven platform that enables users to extract data-driven insights through a One Health lens from all the published research on COVID-19.
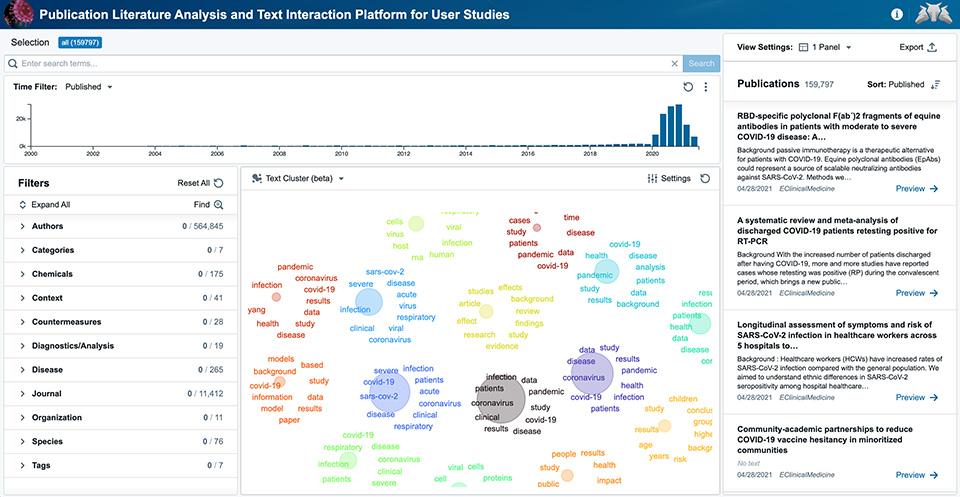
Medical and health intelligence for early warning
MedINT (Medical Intelligence) is a platform that integrates eight data sources on human, society, animal, and weather activities. The dashboard provides early warning and anomaly detection, as well as within a virtually assisted tool for deeper data investigation.
This flexible platform is based on data science, software engineering, and analytic visualization tools that enable detection, tracking, characterization, and situational assessment of events that have the potential to, or are currently causing, harm to human, animal, or plant health.
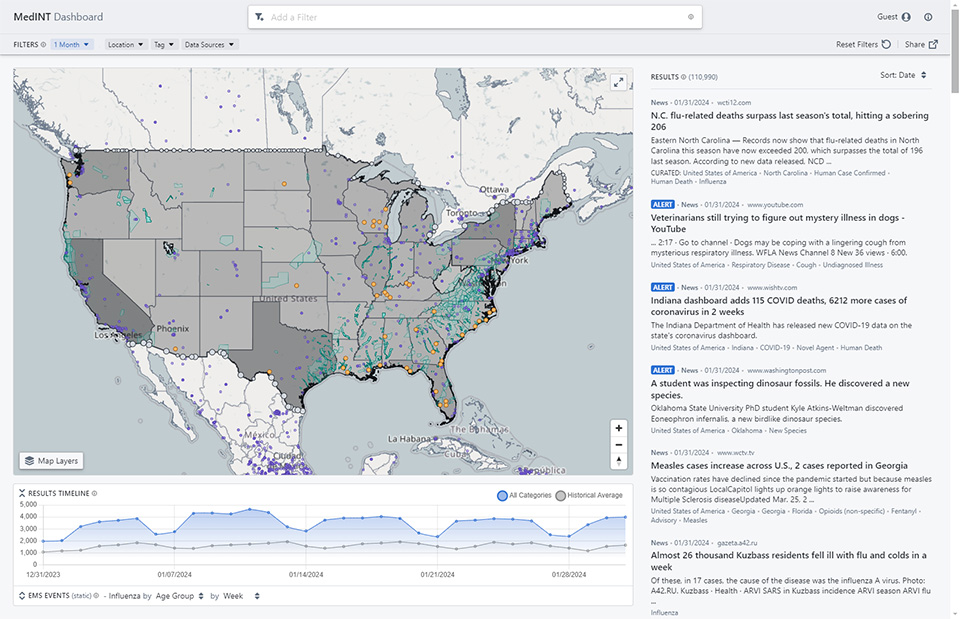
PNNL’s OH TREADS (Threat Risk Event Analysis, Detection and Surveillance Framework) tool is an adaptable capability to meet new and changing needs.
Leveraging MedINT capabilities, OH TREADS integrates 16 additional data types on animal and environmental information and includes a forecasting risk map tool called Planner.
OH TREADS combines a variety of different types of data and AI/machine learning (ML) techniques to provide situational awareness, threat prediction, and risk assessment to a variety of end users.
The long-term goal is to develop a secure, global platform that:
- Creates interoperability of data sources across the One Health landscape
- Provides real-time situational awareness of potential and emerging health threats
- Builds upon trustworthy and explainable AI predictions
- Supports machine augmented decision-making
- Enables cross-agency information sharing and collaboration.
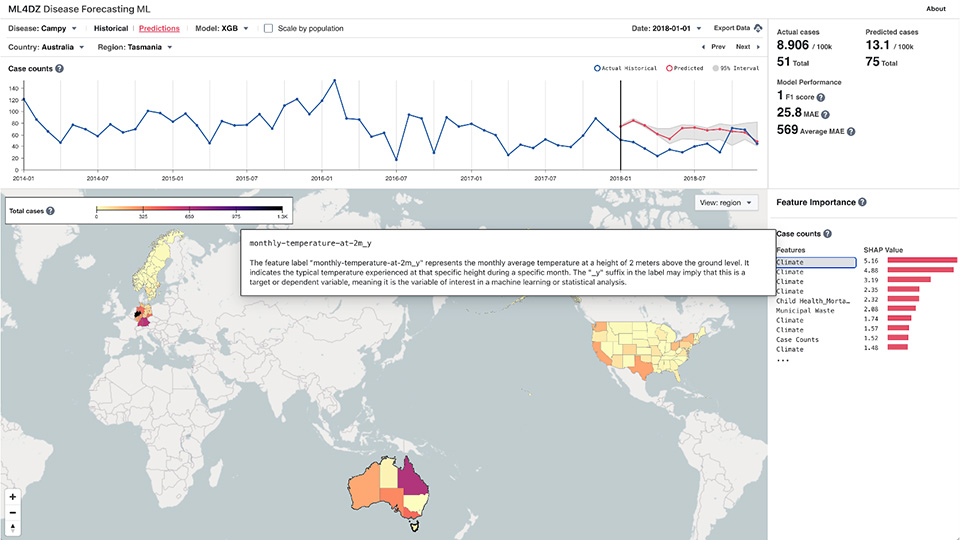
For generalized disease forecasting, Machine Learning for Disease (ML4Dz) is a disease-forecasting system containing multiple AI/ML models. It generalizes global locations and various diseases through the integration of nearly 2,000 features across the One Health landscape.
National Wildlife Disease Database System
PNNL is working with the U.S. Geological Survey to develop a congressionally mandated National Wildlife Disease Database (NWDD) system to ultimately have better situational awareness and early warning for potential zoonotic disease threats from wildlife. This relationship flourished out of the Global Wildlife Data Sharing Conference held at PNNL in 2024, which brought together international, federal, and state agencies along with private, academic, and nonprofit corporations. The conference fostered trust amongst the scientific community and has led to multiple promising data sharing agreements and collaborations.
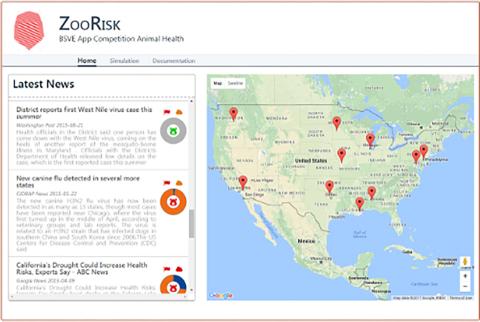
ZooRisk predicts the risk of zoonotic spillover using open-source news, livestock events, and human and animal population data.
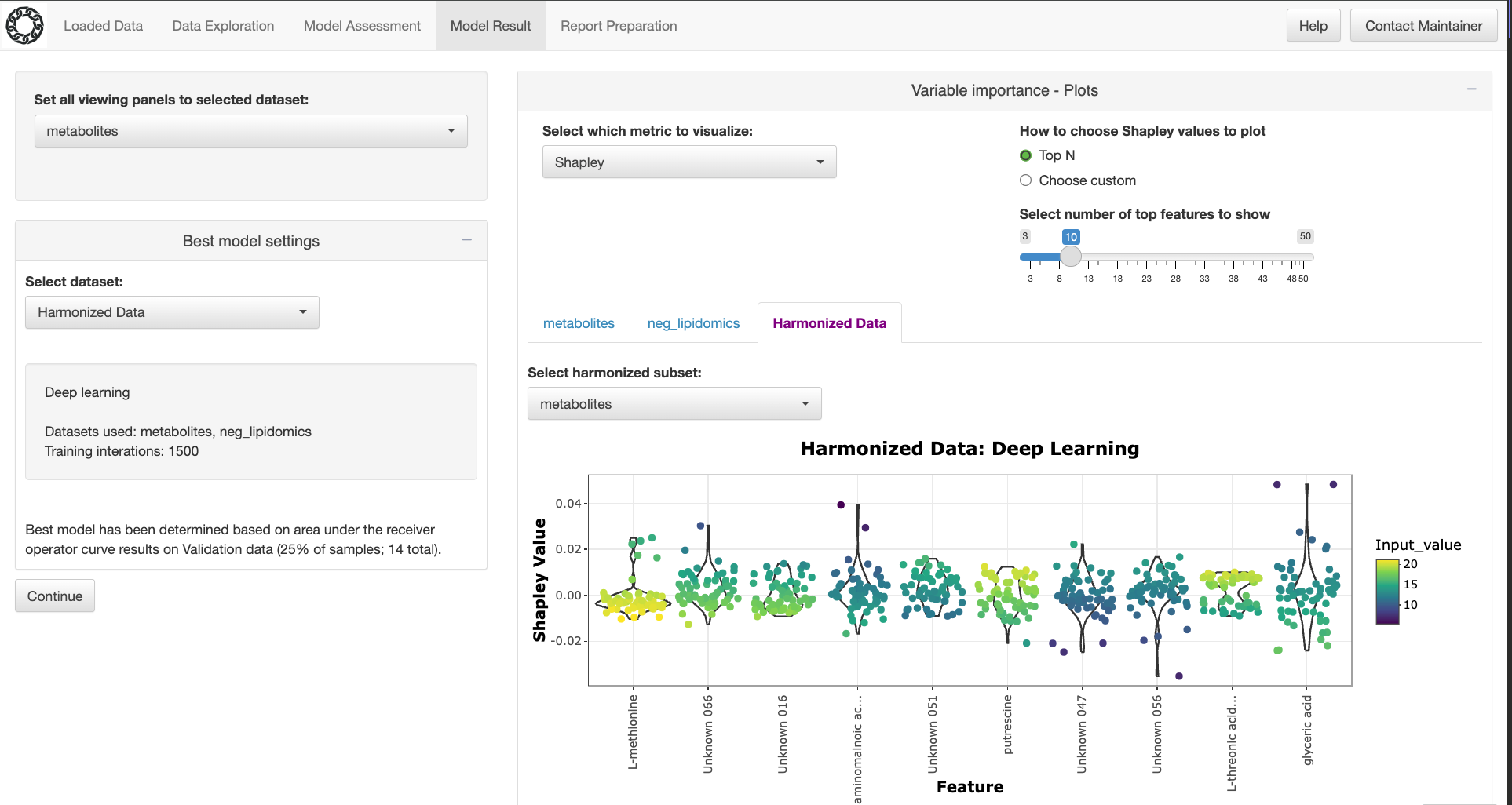
CHAIN (Chem-bio Harmonization with Artificial Intelligence and Networks) is a software tool that harmonizes complex and heterogenous datasets. Using deep learning/ML and network methods, it enables users to explore data, discover complex relationships and patterns among data sources, and visualize data and model results with metrics of uncertainty and insights into model reasoning. Data supported by this application spans a variety of sensor types, including mass spectrometry based ‘omics, Raman spectroscopy, ion mobility spectrometry, infrared spectroscopy, and photoionization detectors.
The Trustworthy Rapid Approvals of Countermeasures (TRAC) project is a new multi-laboratory collaboration. PNNL is developing an AI data management system to extract, harmonize, and correlate across multimodal, cross-domain datasets.
Risk analysis
Food Ag Risk Models (FARM) include risk models that calculate the consequence and/or risk of disease and cyberattacks to food and agricultural facilities using a One Health approach.