Wide-Area Oscillation Assessment and Trending Analysis
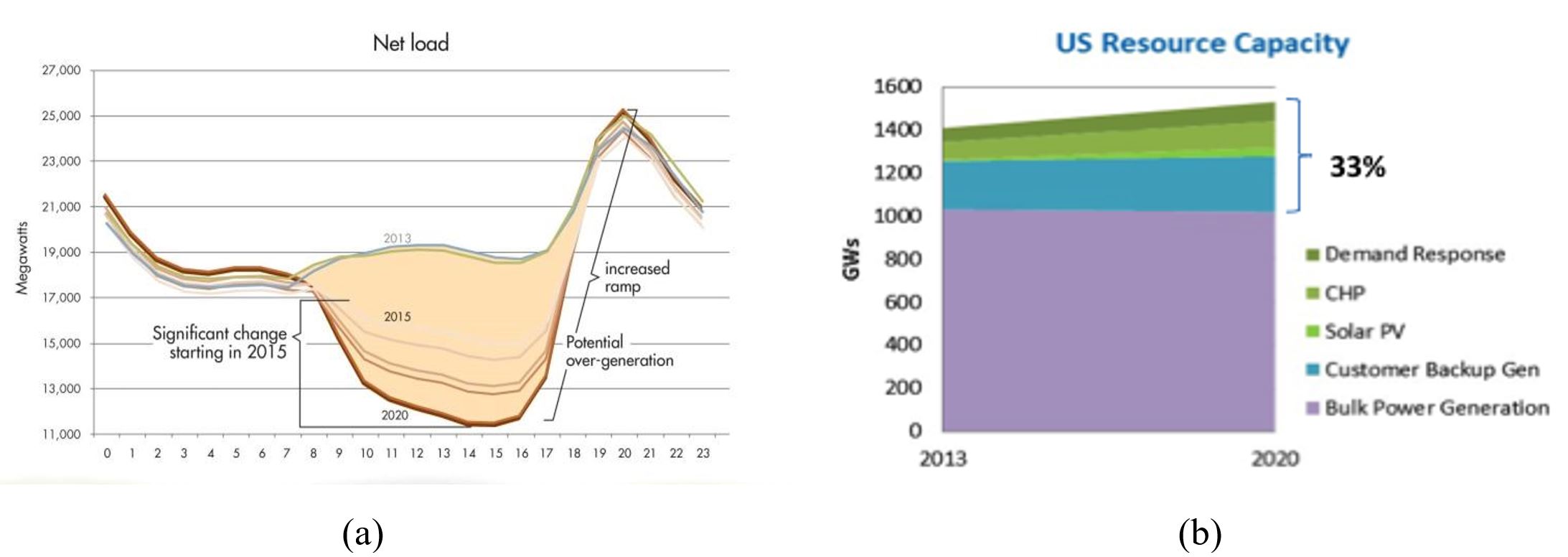
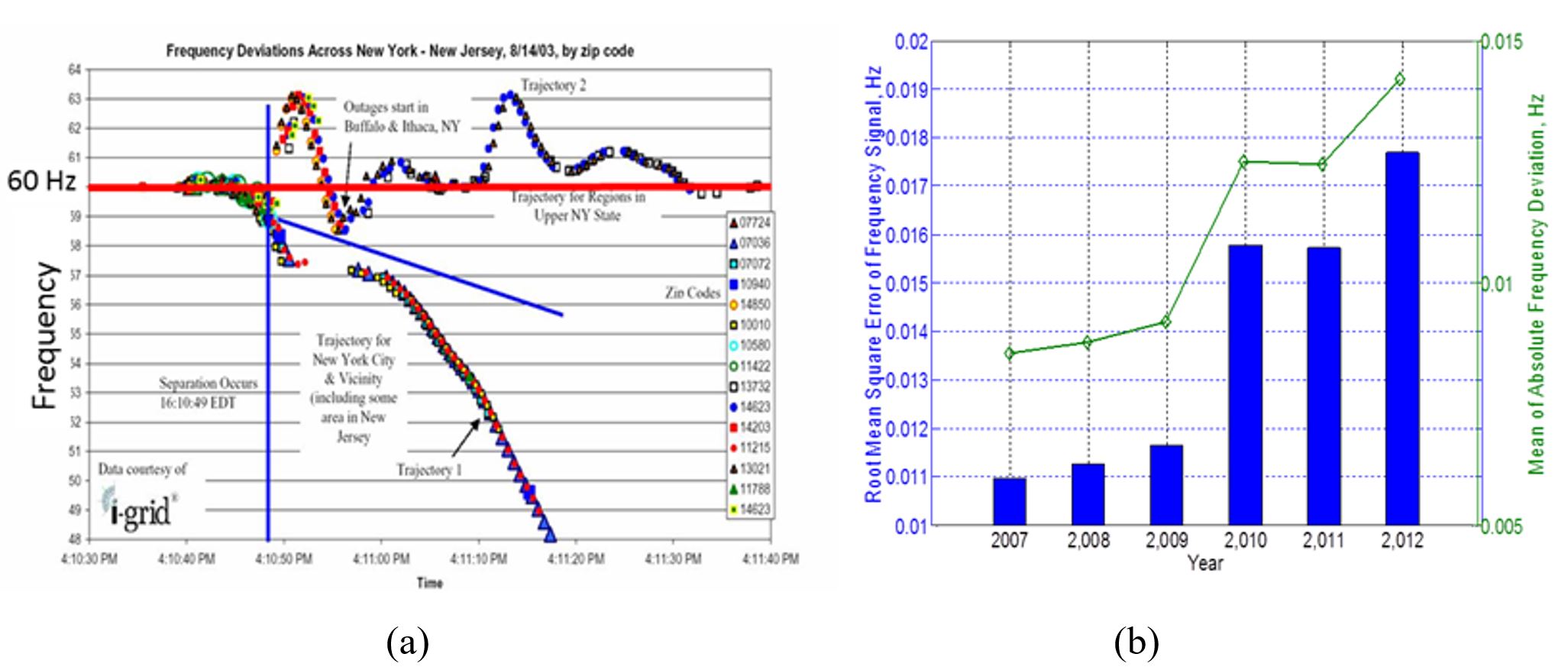
Understanding the potential impact of the on-going power system transition on system modal properties and wide-area oscillatory behavior.

Photo by American Public Power Association on Unsplash