Technology Overview
This innovative technology introduces a contactless sealing mechanism for magic angle spinning (MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, facilitating both slow and fast sample spinning. This novel design eliminates fluid leakage, ensuring more accurate and stable sample analysis, thus enhancing the relevancy of MAS NMR in biomedical and catalytic applications.
In industries utilizing MAS NMR spectroscopy, flow-based cells can encounter fluid leakage during sample spinning, posing a significant challenge and leading to inaccurate analysis and reduced efficiency. This issue is particularly impactful for applications requiring constant flow and high-precision conditions.
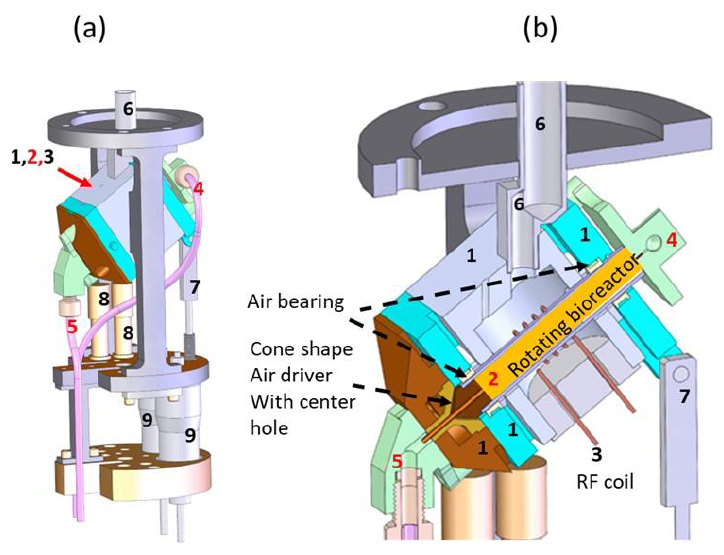
Researchers at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory have developed a contactless sealing system tailored for constant-flow MAS NMR spectroscopy. The novel sealing method prevents leakage at spinning rates ranging from a few hertz up to several kilohertz. The sample spinning setup includes a stationary capillary tube and a rotating bioreactor designed to maintain nutrient and perfusate flow without leakage. Testing with a prototype (glass capillary tubing) has shown stable spinning rates up to 3 kHz.
This innovation addresses core industry problems by enhancing the precision and stability of MAS NMR spectroscopy, resulting in more accurate sample analysis and improved overall efficiency. Potential economic benefits include reduced operational costs and increased reliability of analytical results.
APPLICABILITY
This technology can be widely used in the field of analytical instrumentation, particularly for industries involved in catalysis research and biomedical applications requiring long-term live tissue or cell culture studies.
DESIGN
The schematics of the initial design of the proposed slow-MAS NMR probe with a rotating bioreactor to be built on a 300 MHz NMR system.
Patent Pending.
Advantages
- Ensures fluid-tight seal during high-speed and slow-speed sample spinning.
- Enhances the precision and stability of MAS NMR spectroscopy.
- Facilitates constant-flow operando MAS NMR spectroscopy.
- Has broad potential applications, including catalysis and biomedical research.
For more information, please contact: commercialization@pnnl.gov